FlowLayout
The lecture notes demonstrates how to use FlowLayout.
You must read How to Use FlowLayout
FlowTest.java
You can get the program here .
The output of the program is

1:import java.awt.*;
2:import javax.swing.*;
3:
4:public class FlowTest extends JFrame {
5: JButton[] buttons = new JButton[11];
6: Container contentPane;
7: public FlowTest() {
8: contentPane = getContentPane();
9: contentPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
10: for(int i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
11: buttons[i] = new JButton(Integer.toString(i));
12: contentPane.add(buttons[i]);
13: }
14: }
15:
16:
17:
18: public static void main(String[] args) {
19: FlowTest f = new FlowTest();
20: f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
21: f.setSize(250,150);
22: f.setVisible(true);
23: }
24:}
After you resize it, the windows can look like
Constructors
The FlowLayout class has three constructors:
public FlowLayout()
public FlowLayout(int alignment)
public FlowLayout(int alignment, int horizontalGap, int verticalGap)
The alignment argument can have the value
FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.CENTER, or FlowLayout.RIGHT.
The horizontalGap and verticalGap arguments specify the
number of pixels to put between components.
If you don't specify a gap value, FlowLayout uses 5 for the default gap value.
If you don't specify an alignment, FlowLayout uses FlowLayout.CENTER.
Let take a look at another example first before we go on our discussion.
FlowTest2.java
Get the program here
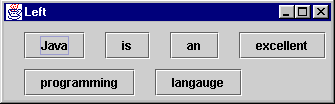
1:import java.awt.*;
2:import javax.swing.*;
3:
4:public class FlowTest2 extends JFrame {
5: String[] strings = {"Java", "is", "an", "excellent", "programming", "langauge"};
6: JButton[] buttons = new JButton[strings.length];
7: Container contentPane;
8: public FlowTest2() {
9: super("Left");
10: contentPane = getContentPane();
11: contentPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT,20,10));
12: for(int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
13: buttons[i] = new JButton(strings[i]);
14: contentPane.add(buttons[i]);
15: }
16: }
17:
18:
19:
20: public static void main(String[] args) {
21: FlowTest2 f = new FlowTest2();
22: f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
23: f.setSize(250,150);
24: f.setVisible(true);
25: }
26:}
How FlowLayout works ?
FlowLayout puts components in a row, sized at their preferred size.
If the horizontal space in the container is too small to put all the components in one row,
FlowLayout uses multiple rows.
Within each row, components are centered (the default), left-aligned, or
right-aligned as specified when the FlowLayout is created.
How to set the alignment?
void setAlignment(int alignment):Sets the alignment.int getAlignment(): Gets the alignment for this layout.int getHgap(),void setHgap(int hgap), int getVgap(),void setVgap(int vgap)
How to add components?
add(Component comp):Adds the specified component to the end of
this container.
Warning: Remember to add the components to
contentPane!!!
Can I insert a component?
Yes. Use add(Component comp, int index). index starts
from 0. Take a look at this example
FlowTest3.java
Get the program here.
Notice I use right alignment in the program.
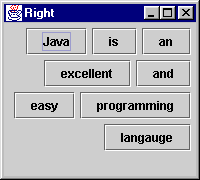
1:import java.awt.*;
2:import javax.swing.*;
3:
4:public class FlowTest3 extends JFrame {
5: String[] strings = {"Java", "is", "an", "excellent", "programming", "langauge"};
6: JButton[] buttons = new JButton[strings.length];
7: Container contentPane;
8: public FlowTest3() {
9: super("Right");
10: contentPane = getContentPane();
11: // I use right alignment
12: contentPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
13: for(int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
14: buttons[i] = new JButton(strings[i]);
15: contentPane.add(buttons[i]);
16: }
17: contentPane.add(new JButton("and"), 4); // add after button "excellent"
18: contentPane.add(new JButton("easy"), 5); // add after button "and"
19: }
20:
21:
22:
23: public static void main(String[] args) {
24: FlowTest3 f = new FlowTest3();
25: f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
26: f.setSize(200,180);
27: f.setVisible(true);
28: }
29:}
How to remove components?
Use remove(int index).
FlowTest4.java
Get the program here .
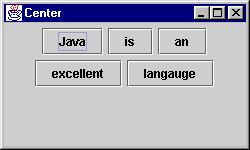 .
.
1:import java.awt.*;
2:import javax.swing.*;
3:
4:public class FlowTest4 extends JFrame {
5: String[] strings = {"Java", "is", "an", "excellent", "programming", "langauge"};
6: JButton[] buttons = new JButton[strings.length];
7: Container contentPane;
8: public FlowTest4() {
9: super("Center");
10: contentPane = getContentPane();
11: contentPane.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
12: for(int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
13: buttons[i] = new JButton(strings[i]);
14: contentPane.add(buttons[i]);
15: }
16: contentPane.remove(4); // remove "programming"
17: }
18:
19:
20:
21: public static void main(String[] args) {
22: FlowTest4 f = new FlowTest4();
23: f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
24: f.setSize(250,150);
25: f.setVisible(true);
26: }
27:}
Summary
- Set
contentPane = getContentPane(). Everying is added or
removed through the contentPane.
- Use
contentPane.setLayout(...) to set the layout.
- Use
contentPane.add(comp) to add component.
- Use
contentPane.add(comp,index) to insert.
- Use
contentPane.remove(index) to remove.
- We can use different aligment.
- We can set the vertical gap and horizontal gap.









 .
.